This site is intended for U.S. residents only
This site is intended for U.S. residents only


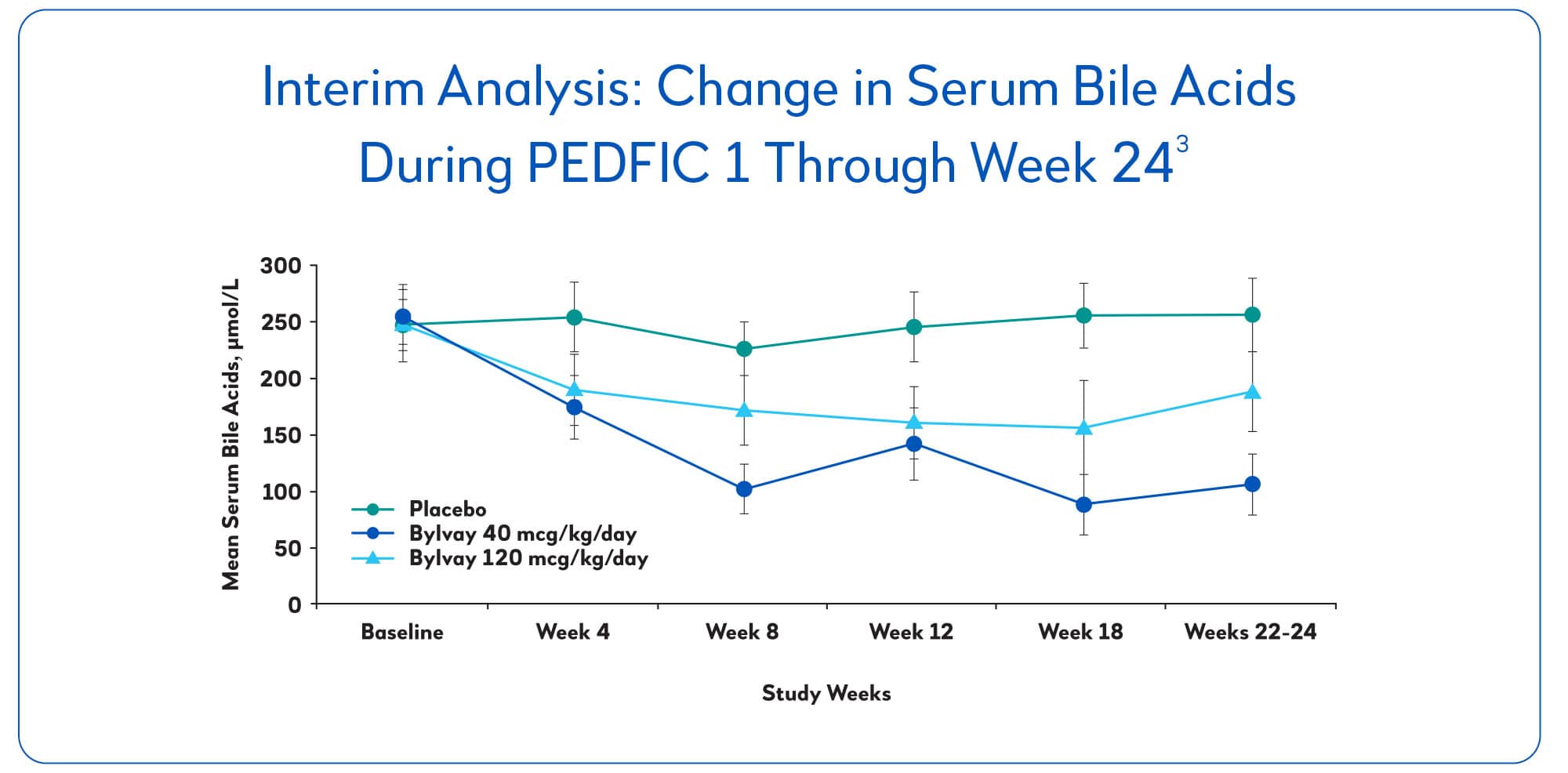
Bylvay improved serum bile acids within 4 to 8 weeks and maintained its effect over 24 weeks of treatment.2
44% at least 70% reduction
In patients treated with Bylvay at 40 mcg/kg/day, 44% reached the secondary endpoint of at least a 70% reduction in fasting serum bile acid levels or reached a level of ≤70 mcmol/L.3
40% lower
sBA levels
Among patients who responded, Bylvay lowered sBA levels >40% on average, from 252 mcmol/L to 145 mcmol/L.3
1. Karpen SJ. Hepatol Int. 2020;14(5):677-689.
2. Bylvay prescribing information. Albireo Pharma, Inc.
3. Data on file. Albireo Pharma, Inc.
Warnings and Precautions:
Liver Test Abnormalities
Patients enrolled in PFIC and ALGS clinical trials had abnormal
liver tests at baseline. In clinical trials, treatment-emergent
elevations of liver tests or worsening of liver tests relative to
baseline values were observed during the clinical trials.
In a clinical trial with PFIC patients, treatment-emergent elevations of liver tests or worsening of liver tests relative to baseline values were observed during the clinical trial. Most abnormalities included elevations in AST, ALT, or total and direct bilirubin. Treatment interruption days ranged from 3 days to 124 days; no PFIC patients permanently discontinued treatment due to liver test abnormalities.
In a clinical trial with ALGS patients, treatment-emergent elevations or worsening in liver tests relative to baseline values were observed during the trial. Most abnormalities included elevations in ALT or AST. One ALGS patient interrupted treatment for 40 days; no ALGS patients permanently discontinued treatment due to liver test abnormalities.
Obtain baseline liver tests and monitor during treatment. Dose reduction or treatment interruption may be required if abnormalities occur. For persistent or recurrent liver test abnormalities, consider treatment discontinuation.
Bylvay was not evaluated in PFIC or ALGS patients with cirrhosis. Closely monitor for liver test abnormalities; permanently discontinue Bylvay if a patient progresses to portal hypertension or experiences a hepatic decompensation event.
Diarrhea
In a PFIC clinical trial, diarrhea was reported in 2 (10%)
placebo-treated patients, 9 (39%) Bylvay-treated 40 mcg/kg/day
patients, and 4 (21%) Bylvay-treated
120 mcg/kg/day patients. Treatment
interruption due to diarrhea occurred in 2 patients with 3 events
during treatment with Bylvay 120 mcg/kg/day. Treatment interruption
due to diarrhea ranged between 3 to 7 days. One patient treated with
Bylvay 120 mcg/kg/day withdrew from the pivotal clinical trial due
to persistent diarrhea.
In an ALGS clinical trial, diarrhea in ALGS patients was reported in 1 (6%) placebo-treated patient and in 10 (29%) Bylvay-treated patients. No patients interrupted or permanently discontinued Bylvay due to diarrhea.
If diarrhea occurs, monitor for dehydration and treat promptly. Interrupt Bylvay dosing if a patient experiences persistent diarrhea. Restart Bylvay at 40 mcg/kg/day when diarrhea resolves and increase the dose as tolerated if appropriate. If diarrhea persists and no alternate etiology is identified, stop Bylvay treatment.
Fat-Soluble Vitamin (FSV) Deficiency
Fat-soluble vitamins (FSV) include vitamin A, D, E, and K (measured
using INR levels). PFIC patients can have FSV deficiency at
baseline. Bylvay may affect absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. In a
clinical trial, new onset or worsening of existing FSV deficiency
was reported in 1 (5%) placebo-treated patient and 3 (16%)
Bylvay-treated 120 mcg/kg/day patients; none of the Bylvay-treated
40 mcg/kg/day patients had new onset or worsening of existing FSV
deficiency. In an ALGS clinical trial, new or worsening of existing
FSV deficiency was reported in 3 (17.6%) placebo-treated patients
and 3 (8.6%) Bylvay-treated patients.
Obtain serum FSV levels at baseline and monitor during treatment, along with any clinical manifestations. If FSV deficiency is diagnosed, supplement with FSV. Discontinue Bylvay if FSV deficiency persists or worsens despite adequate FSV supplementation.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions for Bylvay in patients with PFIC
are diarrhea, liver test abnormalities, vomiting, abdominal pain,
and fat-soluble vitamin deficiency.
The most common adverse reactions for Bylvay patients with ALGS are diarrhea, abdominal pain, hematoma, and decreased weight.
Drug Interactions
For patients taking bile acid binding resins, take Bylvay at least 4
hours before or 4 hours after taking a bile acid binding resin.
Use in Specific Populations
There are no human data on Bylvay use in pregnant persons to
establish a drug-associated risk of major birth defects,
miscarriage, or adverse developmental outcomes. Based on findings
from animal reproduction studies, Bylvay may cause cardiac
malformations when a fetus is exposed during pregnancy. There is a
pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in
women exposed to Bylvay during pregnancy. For more information,
please call
1-855-252-4736.
Bylvay is an ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of cholestatic pruritus in:
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Warnings and Precautions:
Liver Test Abnormalities
Patients enrolled in PFIC and ALGS clinical trials had abnormal
liver tests at baseline. In clinical trials, treatment-emergent
elevations of liver tests or worsening of liver tests relative to
baseline values were observed during the clinical trials.
In a clinical trial with PFIC patients, treatment-emergent elevations of liver tests or worsening of liver tests relative to baseline values were observed during the clinical trial. Most abnormalities included elevations in AST, ALT, or total and direct bilirubin. Treatment interruption days ranged from 3 days to 124 days; no PFIC patients permanently discontinued treatment due to liver test abnormalities.
In a clinical trial with ALGS patients, treatment-emergent elevations or worsening in liver tests relative to baseline values were observed during the trial. Most abnormalities included elevations in ALT or AST. One ALGS patient interrupted treatment for 40 days; no ALGS patients permanently discontinued treatment due to liver test abnormalities.
Obtain baseline liver tests and monitor during treatment. Dose reduction or treatment interruption may be required if abnormalities occur. For persistent or recurrent liver test abnormalities, consider treatment discontinuation.
Bylvay was not evaluated in PFIC or ALGS patients with cirrhosis. Closely monitor for liver test abnormalities; permanently discontinue Bylvay if a patient progresses to portal hypertension or experiences a hepatic decompensation event.
Diarrhea
In a PFIC clinical trial, diarrhea was reported in 2 (10%)
placebo-treated patients, 9 (39%) Bylvay-treated 40 mcg/kg/day
patients, and 4 (21%) Bylvay-treated
120 mcg/kg/day patients. Treatment
interruption due to diarrhea occurred in 2 patients with 3 events
during treatment with Bylvay 120 mcg/kg/day. Treatment interruption
due to diarrhea ranged between 3 to 7 days. One patient treated with
Bylvay 120 mcg/kg/day withdrew from the pivotal clinical trial due
to persistent diarrhea.
In an ALGS clinical trial, diarrhea in ALGS patients was reported in 1 (6%) placebo-treated patient and in 10 (29%) Bylvay-treated patients. No patients interrupted or permanently discontinued Bylvay due to diarrhea.
If diarrhea occurs, monitor for dehydration and treat promptly. Interrupt Bylvay dosing if a patient experiences persistent diarrhea. Restart Bylvay at 40 mcg/kg/day when diarrhea resolves and increase the dose as tolerated if appropriate. If diarrhea persists and no alternate etiology is identified, stop Bylvay treatment.
Fat-Soluble Vitamin (FSV) Deficiency
Fat-soluble vitamins (FSV) include vitamin A, D, E, and K (measured
using INR levels). PFIC patients can have FSV deficiency at
baseline. Bylvay may affect absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. In a
clinical trial, new onset or worsening of existing FSV deficiency
was reported in 1 (5%) placebo-treated patient and 3 (16%)
Bylvay-treated 120 mcg/kg/day patients; none of the Bylvay-treated
40 mcg/kg/day patients had new onset or worsening of existing FSV
deficiency. In an ALGS clinical trial, new or worsening of existing
FSV deficiency was reported in 3 (17.6%) placebo-treated patients
and 3 (8.6%) Bylvay-treated patients.
Obtain serum FSV levels at baseline and monitor during treatment, along with any clinical manifestations. If FSV deficiency is diagnosed, supplement with FSV. Discontinue Bylvay if FSV deficiency persists or worsens despite adequate FSV supplementation.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions for Bylvay in patients with PFIC
are diarrhea, liver test abnormalities, vomiting, abdominal pain,
and fat-soluble vitamin deficiency.
The most common adverse reactions for Bylvay patients with ALGS are diarrhea, abdominal pain, hematoma, and decreased weight.
Drug Interactions
For patients taking bile acid binding resins, take Bylvay at least 4
hours before or 4 hours after taking a bile acid binding resin.
Use in Specific Populations
There are no human data on Bylvay use in pregnant persons to
establish a drug-associated risk of major birth defects,
miscarriage, or adverse developmental outcomes. Based on findings
from animal reproduction studies, Bylvay may cause cardiac
malformations when a fetus is exposed during pregnancy. There is a
pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in
women exposed to Bylvay during pregnancy. For more information,
please call
1-855-252-4736.
Bylvay is an ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of cholestatic pruritus in:
Please see full Prescribing Information.